RAM Speed Calculator
Calculate Ram speed clock interval in nanosecond format
0 ns
RAM speed vs. RAM latency
While a RAM’s data transfer rate tells you how many mega transfers (1,000,000 data transfers) the RAM can do in one second (a DDR4-3200 RAM can conduct 3,200 mega transfers in 1 second), its CAS latency is also important for understanding RAM performance.
CAS latency tells you the total number of cycles it takes for the RAM to send data, but you should also consider the duration of each cycle to get a better idea of that RAM’s overall latency.
Simply, Lower latency is faster.
Finding the RAM specification
Several program such as CPU-Z or Speccy will tell your RAM speed. But, if you're having difficulties on finding ram timing (CL/CAS), it usually printed on the RAM itself. The label example as shown below.
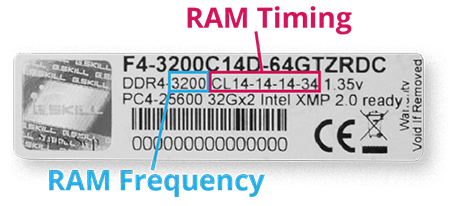
RAM frequency
Ram speed or Frequency usually written on label right after the
RAM type. In the example above, it's DDR4-3200 or
the frequency is 3200MHz. In PC4 Specification, the
frequency is multiplied by 8, so it reads PC4-25600,
denotes overall transfer rate, in megabytes per second. In
computer readings, it's normal if the speed reads half of it,
such as 1600Mhz for 3200Mhz because of
DDR(Double Data Rate). Obvious isn't it?
RAM timing
Column Address Strobe (CAS) latency can be
referred to in several different ways. A RAM kit with a CAS
latency of 14, for example, can be described as CAS 14 or CL14 or
as having CAS 14 timings. To get the CAS/CL, just
look at RAM Label, and you'll find CL14-14-14-34.
The first parameter will be the CL/CAS latency,
which is 14.
This timing specification is standardized by JEDEC, more about it here.